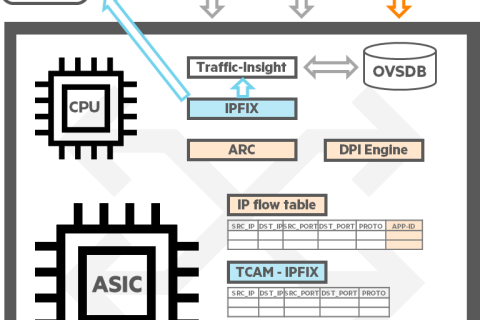
Last timeIn the data center, there is a strong hardware productsWe talked about it.
While physical equipment like servers, storage, and switches are important, it is the computing power that runs on top of this hardware that makes a data center truly ‘smart.’ Various technologiesIt will be.
Data Center TechnologyIran, simply put, is a set of several switches ProtocolIt means to hear.
These protocols are the core of the data center. Efficiently support applications and workflowsIt is essential to do so.
In this section, we'll delve into how data center technology provides the following critical capabilities:.
- Supports multiple tenants (user groups) simultaneouslyHow to do
- Network overlay technologyHow it works with
- Ethernet fabric technologyThe process of creating
- Storage ConvergenceHow to provide
- Data Center Interconnect (DCI) TechnologyDescription of
Understanding these technologies will help you understand how data centers can flexibly handle complex requirements and maintain optimal performance.
So, shall we delve into the world of data center technology together?
Data Center Technology Overview: Understanding Layers
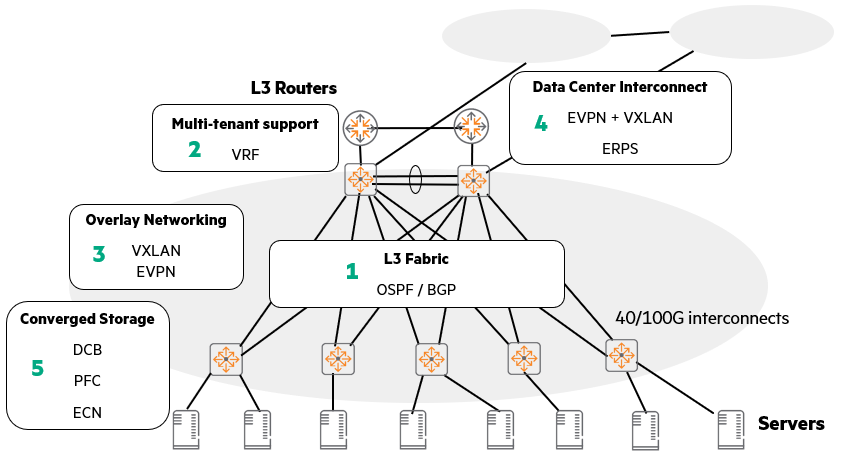
The diagram above provides a quick overview of how data center technologies are interconnected and utilized.
It may seem complicated, but if you break it down piece by piece, it's not difficult at all. Think of it as building a building, layer by layer.
1. The bottom layer, the underlay layer 3 fabric
Like the solid foundation of a building, the most fundamental part of a data center network is the L3 (Layer 3) fabric.
This is handled by routing protocols such as OSPF and BGP.
These protocols are necessary to create a path for network devices to find each other and exchange data.
It is the starting point of all communication.
2. VRF that supports multi-tenant on top of that
Just as a building is built on a foundation to accommodate multiple tenants, to support multiple tenants (logically separated user groups, such as customers or departments) on an underlay network. Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) technologyUse .
VRF creates multiple independent virtual routing tables within a single physical network, allowing each tenant to feel as if they were using their own dedicated network. This segregates traffic so it doesn't mix with other tenants' traffic.
3. Network Expansion, Overlay Networking
Just as corridors and staircases are used to efficiently utilize space in a building, overlay networking technology is used to flexibly expand the network.
Representative examples include VXLAN and EVPN.
By creating a virtual tunnel over the existing underlay network, it allows the network to expand beyond physical constraints and be managed efficiently.
4. Data Center Interconnect (DCI)
If there are multiple buildings, you will need passageways to connect them.
Similarly, EVPN and VXLAN technologies are also important when connecting multiple data centers.
These technologies allow even remote data centers to connect and exchange data as if they were one massive network.
5. Integration of storage and Ethernet, DCB
Finally, in data centers, storage (storage devices) and general network traffic must communicate efficiently over the same Ethernet network.
For this purpose, we use switches that support Data Center Bridging (DCB) technology.
DCB includes features such as Priority-Based Flow Control (PFC) and Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN).
These features prevent traffic loss or slowdowns due to network congestion, ensuring that storage always delivers optimal performance.
Data Center Customer Service Solutions: Tenant-Specific Network Configuration Strategies
When providing services to customers (or departments) from a data center, a strategy for configuring the network according to the size and requirements is required.
Your approach will vary depending on how many customers (or tenants) you have and how you want to segment your network.

1. Single-tenant data center
if Traditional enterprise solutionslike Operate only one data centerAnd if there are no other tenants, the configuration is simple.
- Single VLAN space: In general 4094 VLANsA single VLAN space with suffices.
- Connecting to Backup Data Centers: When connecting to a backup data center, an L2 data center interconnect (DCI) may be required.
- Routing services: Usually for a single company Single Layer 3 (L3) routing serviceis enough.
2. Data centers for a limited number of tenants
The data center Limited number of tenantsWhen you only need support, you have several options to consider.
- Single VLAN space + unique VLAN assignment: Use one data center VLAN space, and give each tenant Assign a unique VLANThis is how it works. For example, tenant A is on VLAN 100, tenant B is on VLAN 200, and so on.
- Assign separate VLANs to each tenant: If you want stricter separation, you can give each tenant Allocate 4094 VLAN spacesYou can do it.
In this scenario, each tenant Separated from each other by L2 DCIAnd each tenant Separate L3 routing serviceYou must receive it.
This routing service may be provided by the data center's core equipment or by a separate data center router.
3. Large-scale multi-tenant data centers
Large-scale Multi-tenant data centerA more flexible and scalable approach is needed.
- Using a single VLAN space: If each tenant only needs a few VLANs, a single VLAN space may be sufficient.
- Provide each tenant with its own 4094 VLAN space (a more flexible and scalable alternative): However, a more flexible and scalable alternative is to provide each tenant with: Provides 4094 unique and isolated VLAN spacesIt is to do.
In this case, for each tenant L2 DCI and L3 servicesEach will require a physical data center routing solution that not only provides this, but can also deploy some types of network functions virtualization (NFV).
Multi-tenancy and Isolation: How to Efficiently Divide Your Data Center
The data center is not just a space used by our company.
Sometimes, multiple departments use it together, and sometimes, it provides services to several different clients.
In this situation HPE supports multi-tenant by utilizing various technologies and safely separates (isolates) each tenant from each other.do.
Why should we support multi-tenancy?
The data center common infrastructureThe target audience for providing this service is as follows:.
- Multiple business units: Even within a company, when multiple departments, such as the marketing department, development department, and finance department, need to operate their own systems,
- Multiple customers: When lending IT infrastructure to multiple customers, such as cloud services
- Multiple services: When various services such as web servers, database servers, and storage are located in one data center
If multiple entities are to use the infrastructure together, the most important thing is Technology that 'isolates' data and traffic from being mixed with each otherno see.
Isolation methods: physical isolation and logical isolation
There are two main ways to isolate tenants.
Physical Isolation
This method literally involves purchasing separate hardware equipment for each customer or service, completely separating them.
Simply put, you buy servers, switches, and storage separately for customer A, and then buy equipment separately for customer B.
But this method It has poor scalability. Because as the number of customers increases, we have to keep buying equipment. It will cost a fortune.
Because we need to place a lot of equipment Space is becoming scarce, and power consumption and cooling problems are also becoming more serious.You can do it.
So, it is not a method that is often used in large data centers.
Logical Isolation
This is what most data centers use these days.
It is a way for multiple customers or isolated services to share a common hardware infrastructure.
Physical equipment is used together, but software technology is used to completely separate them logically.
The biggest advantage is that you don't have to buy multiple pieces of equipment. It can significantly reduce initial investment costs (CapEx: Capital Expenditures).
Also, because limited resources are shared by multiple tenants, The return on investment (ROI) is also much higher.
Multi-Tenant Isolation: Understanding VRFs, the Core of Layer 3 (IP)
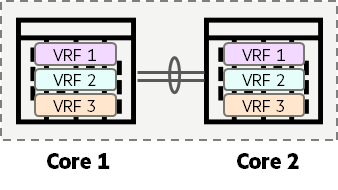
One of the most important techniques for implementing logical isolation is 'Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF)' at the L3 (IP) layer‘ no see.
VRF is literally Technology that 'isolates' Layer 3 routingno see.
You can create multiple independent 'virtual routing instances' within a single physical router or switch.
What does this mean? Each virtual routing instance is like As if there were separate, independent routers It means it works.
That is, Tenant A has its own routing capabilities, and Tenant B has its own routing capabilities.
For each tenant Separate routing tableIt keeps traffic completely separated from each other so that their traffic does not mix or affect the path.
Let's take an example. Let's say your company has a sales team and a development team.
With VRF, even though we physically use a single switch, the sales team has its own network path, and the development team has its own network path. This eliminates any overlap or interference in their IP address space or routing information.
In a single-tenant environment, traditional Layer 3 routing may be sufficient.
These deployments use a single routing table that serves all L3 VLAN interfaces.
For multi-tenant environments, ACLs may be sufficient to secure communication between L3 interfaces of multiple customers.
However, a simple ACL configuration error can expose one tenant's traffic to another.
For this reason, it is recommended to use isolated routing tables in multi-tenant environments.
Then, apply the VRF feature, also known as VRF-Lite, to the AOS-CX device to create a routing instance.
This provides isolated routing tables for tenants generated by different routing protocols.
However, hardware limitations exist!
VRF is a really useful and powerful technology, but there's one important thing to remember.
as soon as ‘Platform hardware limitations still apply.is the point.
For example, if you have a switch device Specifications capable of handling up to 128,000 IPv4 routesLet's say we have .
And I set up 10 VRFs on this device.
In that case, All 10 customer VRF routing tables share the 128,000-row routing table size of this switch.Must do.
That is, no matter how logically separated they are, the performance or capacity limitations of the underlying physical equipment still apply.
Therefore, these hardware limitations must be taken into account when designing and using VRF.
Multi-Tenant Isolation: How to Segment Layer 2 Networks (VLAN vs. VXLAN)
This time Isolate Layer 2 (L2) networksLet's learn how to do it.
The L2 network, also known as the data link layer, is where switches primarily operate.
1. Traditional method: VLAN
The most traditional way to isolate L2 networks is to use Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs).
VLAN allows one physical switch to be divided into multiple logical switches.
This may be sufficient for small to medium-sized data centers, especially privately owned data centers for single tenants.
VSX (Virtual Switching eXtension) is often deployed alongside these traditional VLANs.
Because VSX Significantly improves redundancy of access and core layersBecause they told me to do it.
Link Aggregation between VSX systems can improve bandwidth utilization and further enhance network resiliency.
However, VLANs have two major challenges:.
- Limited number: VLAN is You can only create up to 4094This limit can be problematic in large-scale multi-tenant environments. For situations requiring thousands of customers or numerous logical partitions, 4094 may not be enough.
- VLAN ID duplication issue: Another difficulty is Manage so that each customer (tenant) does not use the same VLAN ID.For example, if Tenant A uses VLAN 10, and Tenant B also uses VLAN 10, a conflict could arise. Preventing this duplication requires complex planning and management.
2. Modern approach: VXLAN (Virtual eXtensible LAN)
The technology that emerged to overcome these limitations of VLAN is VXLAN (Virtual eXtensible LAN).
Provides virtualized VLANs, especially for hypervisor environments (environments with a lot of virtual machines).
- When you assign a virtual machine (VM) to a specific VXLAN, that VM can easily communicate with other VMs belonging to the same VXLAN.
- Since VXLAN is fundamentally a tunneling technology, it requires an integration process to communicate with traditional VLANs.
- The biggest advantage of VXLAN is Supports up to 16 million VXLAN IDsIt is to do.
It provides tremendous scalability, far exceeding the 4094 VLAN limit. - VXLAN uses a single VXLAN ID space.
For example, if a customer uses 100 VLANs, that customer will use 100 VXLAN IDs.
VXLAN and VXLAN + EVPN – Revolutionizing Data Center Networks
This time, it is the technology that truly revolutionizes data center networks. VXLAN과 VXLAN + EVPN Let's learn more about combinations.
Let's explore why these technologies are particularly powerful in data center environments.
1. VXLAN: IP-based Layer 2 extension technology
VXLANBecause it solves problems that do not often occur in traditional campus environments. The biggest advantage in a data center environmentIt exerts its power.
- IP-based L2 overlay: VXLAN is IP-based Layer 2 overlay technologyno see.
Simply put, it is a method of overlaying a virtual Layer 2 network on top of an existing IP network. - ‘'MAC in UDP' encapsulation: This technology encapsulates Layer 2 traffic (MAC frames) within IP datagrams and transmits them using a special format called **"MAC in UDP"**. This significantly improves functionality and scalability.
- Leverage existing IP infrastructure: Once Layer 2 traffic is encapsulated within an IP datagram, it can be transferred to a data center or between data centers without any additional overhead. Leverage any IP routing infrastructureYou will be able to do it.
- Inheriting the benefits of routing infrastructure: Therefore, VXLAN services are provided by existing routing infrastructure. All redundancy, resiliency, and load-sharing capabilitiesThis has the tremendous advantage of being able to utilize it as-is when needed, just like Layer 2 traffic can enjoy the benefits of IP networks.
2. VXLAN's overwhelming scalability
- 24bit VXLAN ID: VXLAN ID is 24-bit valueUse .
This is twice the number of bits available in traditional 802.1q VLANs (12 bits). - Over 16 million VXLAN IDs
- VNI (Virtual Network Identifier): VXLAN is VNIUp to 16 million VXLANs are uniquely identified using numbers, each of which can have its own VLAN.
3. Combining VXLAN and EVPN
VXLAN alone is great, but when you combine it with EVPN (Ethernet VPN), the real synergy explodes.
This combination is especially Large-scale multi-tenant environmentsWe provide innovative solutions such as:.
EVPN (Ethernet VPN) uses MP-BGP (Multiprotocol BGP) between VTEPs (VXLAN Tunnel End Points). Automatically discover and create tunnelsThis allows VMs or customers to be accessed without being restricted by their physical location within the data center. Flexibility to move freelyIt provides.
It's as if the network automatically follows and connects the VM to any physical server.
In this process, VXLAN Actual transmission mechanism for Layer 2 framesis in charge of.
That is, the lower IP network encapsulates Layer 2 frames and transmits them safely and efficiently through the tunnel.
Network overlay feature
Network overlay featureWhat is Iran?
Simply put, it's like adding clothes on top of an existing physical network. Ability to create and provide a 'virtual network' for specific servicesno see.
It is mainly used in virtual machine (VM) based environments.
A representative technology for implementing these overlay networks is VXLAN.
- Provides virtual networks: VXLAN allows each VM or host to: Unique VXLAN ID instead of physical/traditional VLAN IDThis allows for much more flexibility in configuring virtual networks without being constrained by physical location or number of VLAN IDs.
AOS-CX switchis in this VXLAN network VXLAN Tunnel End Points (VXLAN VTEPs) Can perform a role.
VTEP is responsible for encapsulating and decapsulating (returning to original) data packets at the start and end points of a VXLAN tunnel.
Overlay Technology: VXLAN, the Core of Data Center Design
When designing a data center, there are times when 'overlay technology' is absolutely necessary.
The key technology needed at this time is VXLAN (Virtual eXtensible LAN), which has been continuously explained above.
VXLAN: Why is it a good fit for data centers?
- Provides virtual L2 networks: VXLAN is specifically designed to provide a virtual Layer 2 network for virtual machines (VMs) based on a hypervisor (the software that creates and manages virtual machines).
- Driven by VMware and others: This VXLAN protocol was initially VMwareThis technology was developed and promoted by several vendors, including VMware. Initially, it existed only as a "virtual construct" within the VMware hypervisor.
- Now also supports physical switches: now Physical switches such as the CX 8325Of course, some virtual appliances also support VXLAN, allowing for flexible connection between virtual and physical environments.
VXLAN Utilization Scenarios
- Single-Customer Environment:
- If the environment is for a single customer only, Hardware VXLAN gateway capability of the CX 8325 switchavailable for routing
- What is important here is to connect VXLAN to the VLAN of the physical interface. You must bind using VNI (VXLAN Network Identifier)This is the point where communication between physical and virtual networks is possible.
- Multi-Tenant Infrastructure:
- Even in large multi-tenant environments, the CX 8325 switches Hardware VTEP (VXLAN Tunnel End Point) rolecan be performed.
- This allows each data center customer to: Unique set of VLANsYou will be able to have .
This means that while sharing physical resources, each customer's network can be logically and completely separated. - The CX 8325 is Hardware VXLAN gateway roleIt can also be used as a .
Efficiently handles communication between virtualized customer networks and external networks.
Data Center Ethernet Fabric Technology: The Key to High-Speed Connectivity!
Data Center Ethernet Fabric Technologyis in a modern data center Absolutely essential elementno see.
Because this technology connects everything a data center needs. highwayBecause it is the same.
Beyond simply connecting devices, an Ethernet fabric must provide the following core capabilities:.
- High-speed interconnect: Between servers, storage, and other network equipment within a data center. A connection that can send and receive data at incredibly high speedsProvide
- Efficient path selection: In a data center where numerous devices and paths are intertwined, data can find the fastest and most efficient path to its destination, providing seamless communication without performance degradation.
- Scalability: Ethernet fabrics are designed to scale Provide sufficient bandwidthAnd every time new links are added To maximize the usability of existing links Need to design
Server Access Layer: Where Storage and Network Meet: Converged Storage
How you connect and manage storage (storage devices) on your servers has a critical impact on data center performance.
In particular, the concept of converged storage means integrating storage traffic and general network traffic onto the same Ethernet network.
iSCSI (Internet Small Computer Systems Interface)
iSCSIIt is a technology that 'encapsulates' traditional SCSI protocol communication within TCP/IP packets, and then transmits these TCP/IP packets by encapsulating them again within Ethernet frames.
Simply put, it allows existing storage communication methods to be exchanged over a general Ethernet network.
The iSCSI protocol does not require DCB or any other special Ethernet enhancement protocols.
Instead, it is based on features inherent in the TCP/IP protocol stack itself, such as TCP characteristics that ensure reliable transmission. Mitigates packet loss issues.
In an enterprise environmentFor stable performance, the following are important:.
- Powerful QoS (Quality of Service) features: Ensures stable transmission by giving high priority to storage traffic.
- Hardware switches with enhanced buffer capabilities: Data can be processed without packet loss even when network congestion occurs.
In this case, the iSCSI frame transmission Increase reliability and minimize retransmissionsThis can optimize storage performance.
RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet)
RoCE, as its name suggests, RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) It is a technology that implements technology on top of Ethernet.
RDMA is a technology that allows the network adapter to directly access memory and transfer data without CPU intervention, providing tremendous speed and low latency.
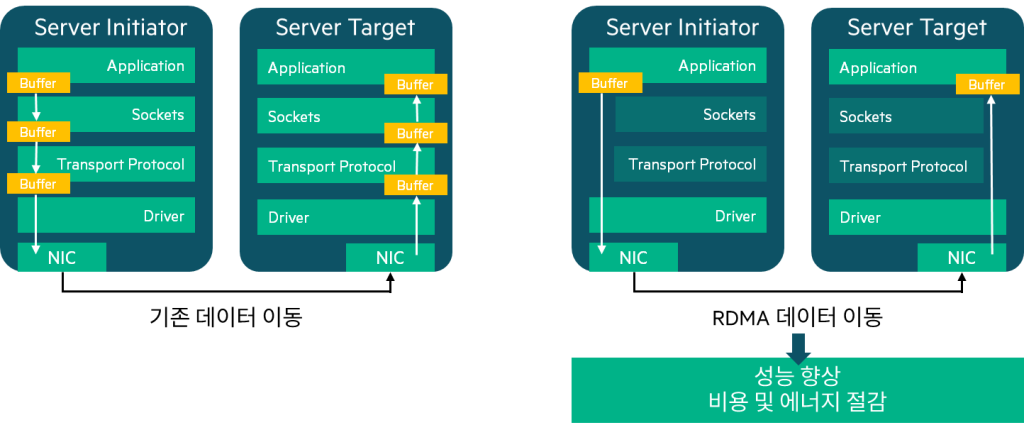
RoCE requires a lossless environment utilizing protocols such as DCB, Priority-Based Flow Control (PFC), and Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN).
Server Access Options: Storage Connectivity Strategies
There are many factors to consider when deciding on server access options, but in particular: Storage Access RequirementsThis is important.
Storage access method
- Dedicated FC (Fibre Channel) network: Using a Fibre Channel network designed specifically for storage
- Converged Storage: Ethernet method that transmits both general data and storage traffic
- iSCSI storage: A method of accessing block-level storage over a TCP/IP-based Ethernet network.
Hypervisor optimization support
Another consideration is Optimized hypervisor (virtualization manager) supportIt is to do.
This can be achieved by supporting multiple paths for the following networks:.
- Hypervisor Management Network
- vMotion network (migration network for VM redundancy)
- VM Network
- Storage Network
Like this, according to each role Separate network pathsBy doing so, we can ensure isolation.
In RAID environments Flex10 network cardYou can use it to increase flexibility.
Protocols to Consider When Planning Storage
When designing a data center NFS, iSCSI, FC, and NVMeoF, etc. Storage protocols must be considered.
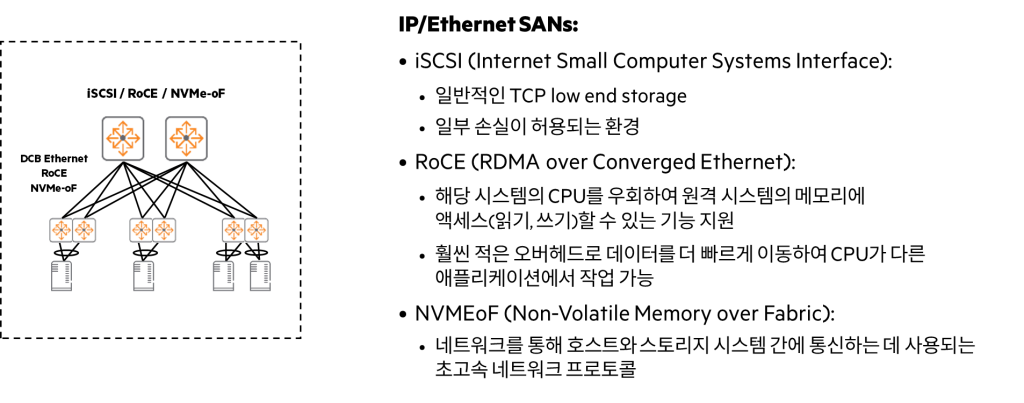
- Storage Protocol: There are new technologies such as NFS, iSCSI, FC, and NVMeoF (NVMe over Fabrics).
- NFS (Network File Systems): NFS bundles multiple storage structures into a single virtual drive, providing file-level access.
There are few special design requirements for NFS deployments.
If you need to ensure stable NFS service, we recommend using a dedicated VLAN and server NIC (network card).
Another option is to share the NIC with other traffic, using Quality of Service (QoS) if necessary to mitigate transmission issues. - iSCSI: iSCSI provides block-level access to storage systems.
The recommended approach is to set up a dedicated VLAN for your iSCSI infrastructure.
Additionally, it is best to use a dedicated switch designed exclusively for storage traffic.
For connectivity, data and iSCSI traffic can share a top-of-rack switch, which can have a dedicated uplink to an Ethernet storage switch. If the same switch and uplink are used, a protocol such as Data Center Bridging (DCB) should be used to prioritize storage traffic and ensure a lossless environment.
Data Center Interconnect (DCI) Technology: Connecting Multiple Data Centers as One
Data Center Interconnect (DCI) Technologyis a core technology that interconnects multiple physical data center sites to ensure seamless customer service. While just two data centers can be connected, multiple data centers can be distributed across different locations for additional scalability and redundancy.
Core Requirements of DCI Technology
These DCI technologies typically require the following options:.
- Path redundancy options: You need to have multiple paths so that if one path fails, traffic can continue to flow through other paths.
- Scalable Layer 2 (L2) connectivity between data centers: Data center networks must provide scalable L2 connectivity to meet all customer requirements, including migrating virtual machines (VMs) to different physical hosts using technologies like VMware's vMotion.
Traditional DCI connection method
There are several traditional ways to connect data centers.
- Dark fiber connection: A method of installing direct fiber optic cables between two sites
- Service Provider's Connection Services: How to utilize the connection service provided by a telecommunications carrier (service provider)
Once these physical connections are established, VLAN Trunk Links and Link Aggregation are configured to connect the core equipment at each site.
Redundancy and load sharing for DCIs on campus or in the region
If your data centers are located within the same campus or region, you can leverage the following technologies:.
- Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS): Provides redundancy with recovery time of less than 50ms in a ring topology.
- Fiber connectivity for ring topology: Connect fibers in a ring topology for redundancy and load sharing.
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP): Provides gateway redundancy for hosts (servers, etc.)
DCI over L3 Infrastructure: VXLAN and EVPN
Recently, data centers Encapsulates L2 traffic between data centers connected via Layer 3 (L3) infrastructure.With the option to do VXLANThis is utilized.
- Role of VXLAN: VXLAN serves to tunnel L2 traffic through L3 networks.
- The role of EVPN: EVPN is for transmitting data between VXLAN tunnel endpoints (VTEPs) with the same VNI. Dynamically create tunnelsThis plays a key role in providing massive L2 scalability, including VM mobility.
In this post, we looked at various technologies used in data centers.
As technologies like virtualization become more widespread, the technologies required to build data center networks have also evolved.
Technologies such as RoCE, along with VXLAN and EVPN, are widely used in modern data center networks, so it is important to be familiar with them.
In particular, the concept of VXLAN, which is explained repeatedly, must be understood before moving on to the next lecture.