Officially launched in July 2023 Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC)was formed to develop Ethernet specifications that enhance AI and high-performance computing (HPC) environments with next-level performance, scalability, and interoperability. Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) is one of the original founders of the UEC., UEC Specification Revision 1.0Contributed a significant portion of the underlying IP to be included.

UEC is laying the foundation for seamless data exchange and computation in the digital domain for today's most critical workloads in IT. Part of UEC Ultra Ethernet Transport (UET)is focused on creating a new L4 transport optimized to enhance both AI and high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
Congestion Control is one of the key technologies defined by UET that aims to maximize link utilization.
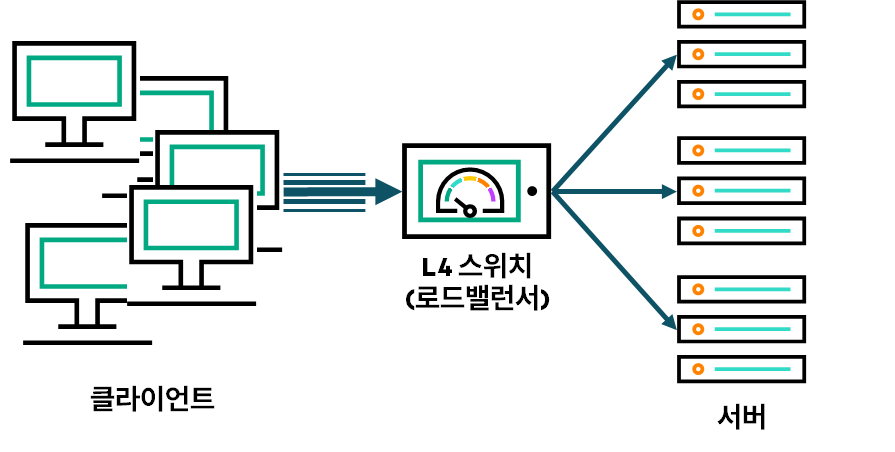
To support this, Dynamic Load Balancing (DLB) is ideal for achieving efficient load balancing and preventing congestion in RoCEv2 networks. HPE Aruba Networking CX switches can be part of this innovation, along with UEC, by integrating with HPE AI/HPC solutions.
AOS-CX switches are designed to support UEC, enabling rapid and seamless adoption of the new UEC protocol across both existing and new solutions. Many essential features, including Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN), are currently supported.
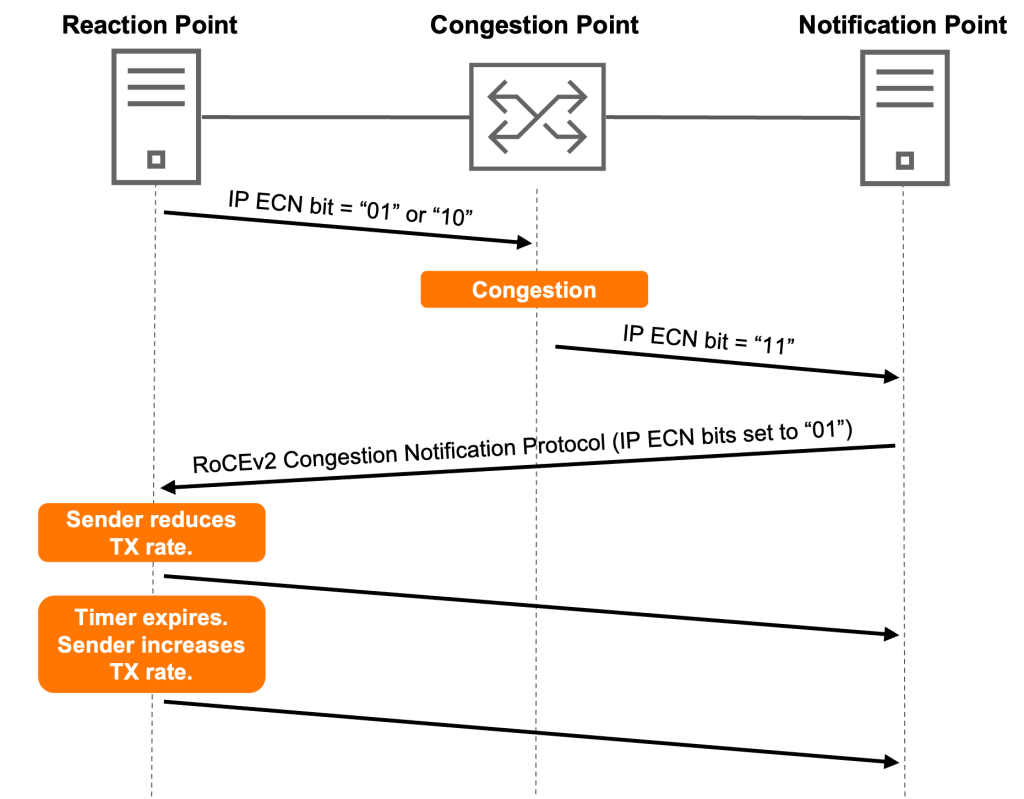
ECN notifies the network of congestion, with the goal of reducing packet loss and latency by allowing the sending device to slow down its transmission rate until the congestion is resolved, without dropping packets. Additionally, HPE Aruba Networking CX switches for data centers include Includes DLB supportIt will work.
DLB is a Dynamic Load Balancing technology, which can be summarized simply as:, The ability to analyze network traffic in real time and distribute it across multiple paths (links, servers, etc.) in the most efficient and balanced manner.no see.
Traditional static load balancing distributes traffic according to predefined rules.
However, this approach fails to distribute traffic when a specific link becomes overloaded or when large amounts of traffic from AI workloads are concentrated on a specific link. Therefore, a feature called DLB plays a key role in high-bandwidth networks like AI fabrics, proactively responding to rapidly changing traffic conditions to efficiently utilize network resources, prevent bottlenecks, and optimize overall system performance.
DLB improves Equal Cost Multi-Path routing (ECMP).
ECMP typically uses a hashing algorithm to load balance traffic across multiple links based on a per-hop decision.
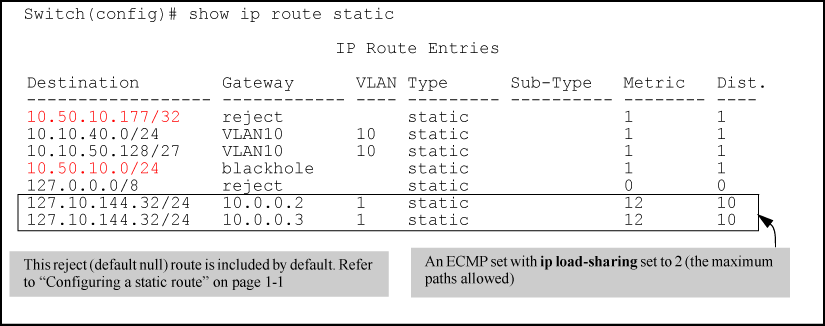
DLB monitors link utilization and rebalances flows based on path utilization, enabling more efficient forwarding and reducing congestion.
HPE Aruba Networking CX 9300 Switch Seriesis Flowlet1 or Packet Spray2Supports DLB based on .

Fast Link Failover (FLF) with DLB moves traffic to a less congested link if the current link fails.
The CX 9300 switch supports AI and HPC networks that use DLB to control network congestion.

Packet trimming3Other optional features, such as , are being considered for addition to HPE Aruba Networking CX switches.
As UEC continues to reimagine Ethernet to support HPC and AI applications that demand increased network performance and efficiency, HPE is continuing to evaluate potential future support on select HPE Aruba Networking CX switches.
HPE Aruba Networking CX switches help you design your network for ultimate reliability, precise control, and peak performance.
When deploying an AI network, you can enable DLB for that AI workload.
As the UEC standard is ratified, HPE Aruba Networking CX Switches are continuously reviewing these standards and exploring their potential for inclusion in select CX switches to fully leverage the potential of Ultra Ethernet and optimize fabrics to future-proof your infrastructure.
- Flowlet: A small unit of data flow.
Large data flows consist of millions of packets, allowing for more granular traffic distribution across the entire flow. ↩︎ - Packet Spray: A technology that distributes and transmits packets within a single data flow through multiple paths.
The concept of dividing packets belonging to a single flow and sending them to multiple links as if sprinkling water. ↩︎ - Packet Trim: A technology that reduces the size of an Ethernet packet by cutting out unnecessary or redundant data from the tail portion of the packet. ↩︎


