In the last post, we looked at various designs for data center networks.
We explained the characteristics of each design, along with its pros and cons, and changes in architecture.
This time, we will look at DCI (Data Center Interconnect), which is a connection between data centers, and OOBM, which is a management network.
Data Center Interconnect (DCI): Technology that connects multiple data centers.
Folks, our customers often operate multiple data centers.
These data centers may be concentrated in one area or distributed across several different locations.
The technology that connects multiple data centers and allows them to function as one large network is called DCI.
Data center designs can leverage a variety of technologies for this interconnection.
Three Key DCI Technologies
Key DCI technologies include:.
- Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS)
- VXLAN/EVPN
- VSX (Virtual Switching eXtension) + Link Aggregation
The figure below shows two active data centers.
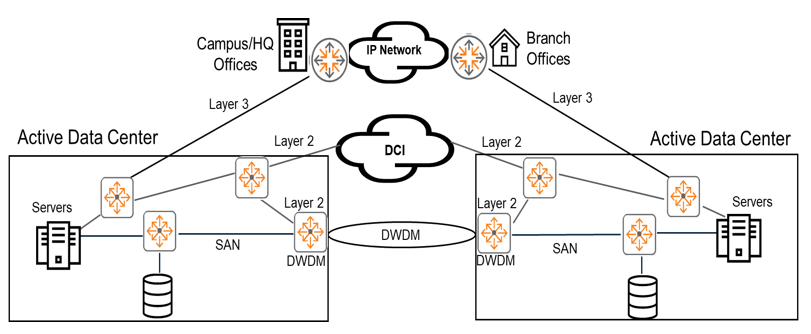
Both on-prem campus and branch offices are connected to these two active data centers, which are connected via Layer 3 protocols.
Layer 3 (IP network) connectivityIt connects different data centers using the Internet or a private network, or provides connectivity to data center services from campus and branch offices. VPNs are often used to secure these communications.
The goal of DCI technology is Connects data centers using Layer 2 protocols, providing low latency and high bandwidth connections.It is to do.
That is, we create a high-speed connection to avoid delays or disconnections when exchanging information between data centers, and we recommend L2 communication for VM movement.
DWDM1is a technology that multiplexes multiple optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber using laser light of different wavelengths (colors).
This technology enables bidirectional communication (also known as wavelength division duplexing) and capacity multiplication over a single optical fiber.
AOS-CX switches do not currently support DWDM directly.
This technology is often provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
DCI using ERPS and VRRP
AOS-CX switches support features such as ERPS, VSX, and VRRP.
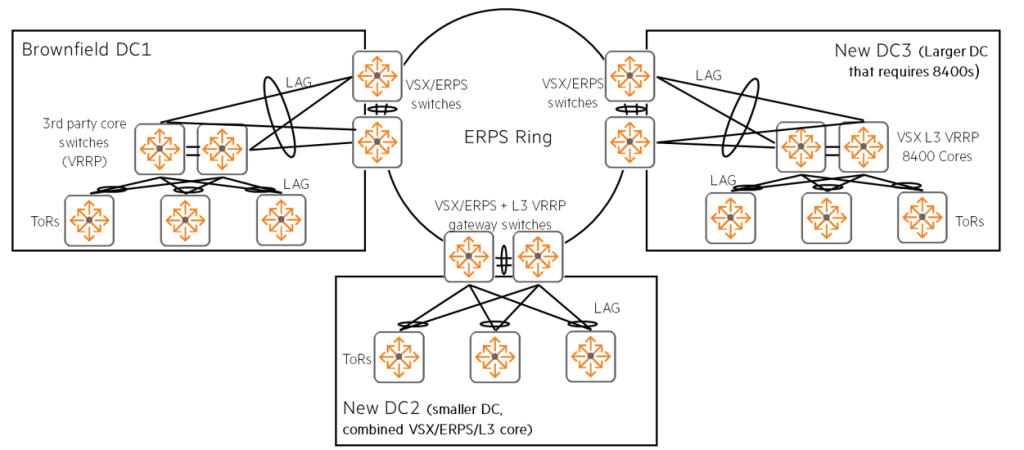
As you can see from this topology, VRRP2 Implement DCI by combining gateways across an ERPS ringYou can do it.
The combination of LACP, L2 ERPS, and L3 VRRP provides L2 and L3 connectivity across multiple data centers. Loop-free network connectionIt provides.
The ERPS ring structure is a data center relatively close distance(in the same campus or city) ring (circular) shapeIt is advantageous when you can connect to it.
VSX within each data center3When combined with ERPS, in case of link or switch failure, High network availability and fast convergence times of less than 1 secondDual control plane LAG to achieve (non-disruptive switching to another path)4in the file.
For example, this solution is dark fiber5 It is suitable for data centers such as Brownfield (existing infrastructure) DC1 supporting third-party switches via connectivity, small DC2 with a combination of VSX/ERPS/VRRP switches, and large DC3 requiring CX 8400 cores.
CX 8320 and CX 8325 series switchesSupports ERPS/VSX DCI from AOS-CX version 10.03, and supports up to 5 data centers (5 x VSX/ERPS switches) in an ERPS ring (10 switches).
DCI using VXLAN and EVPN
VXLAN/EVPNis useful for longer distance connections.
It can connect well even if there is an L3 network such as the Internet in the middle.
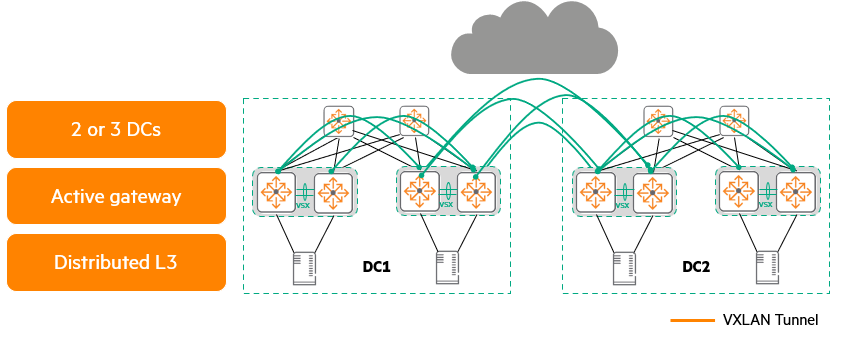
Technologies such as VXLAN and EVPN are also options for DCI, The advantage of being able to go beyond L3 segments such as WAN links.There is this.
Thanks to this, VMs can be moved freely like L2 even in remote environments, and scalability is also good.
As of this writing, up to three data center DCIs are supported using VXLAN/EVPN.
For these deployments, HPE uses Active Gateway (Anycast) to connect data centers. Use a distributed gatewayIt is recommended to do so between data centers. iBGP. Optimally, we recommend using VSX pairs to provide high availability and using ARP/ND suppression to prevent unnecessary data from traversing the WAN link. Keep in mind that WAN links add latency and may have low bandwidth and MTU.
DCI with HPE Aruba Networking VSX and LAG
Deploy multiple VSX systems Connect with link aggregationYou can do it.
mostly Connecting two data centersIt is very useful when doing, When you want to create a high availability network simply great.
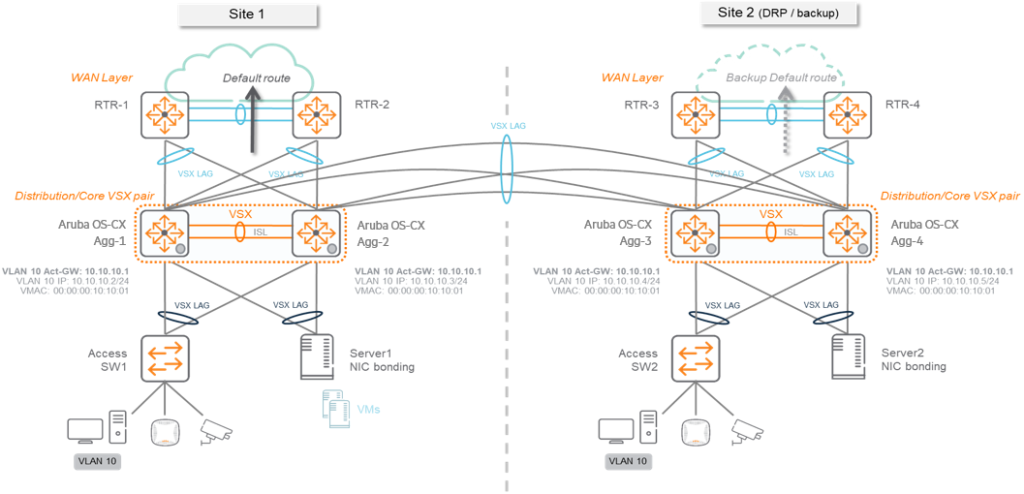
Each data center consists of one VSX system, which can be interconnected using traditional link aggregation.
There must be at least two additional links connecting data centers.
Because each site operates an independent VSX pair, setup and management are very easy, and it provides reliable recovery from switch or cable failures.
Connections can be made using various existing connection methods (1Gbps, 10Gbps, dedicated optical fiber, DWDM, etc.).
Bundle all links using link aggregation to create multiple active/active paths between data centers.
Negotiates and controls aggregated connections using the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP).
Deployments using VSX and link aggregation are very easy to maintain and operate, and switch and link failures are reliably and easily managed.
If your network requires more than one data center, to avoid loops and perform cross-site topology calculations, Specific L2 topology protocolsYou must use .
OOBM Network: A Data Center Management Network for Emergency Situations
In the data center There are several networksI told you.
Storage network, data network (in-band), and this OOBM (Out-of-band Management) networkno see.
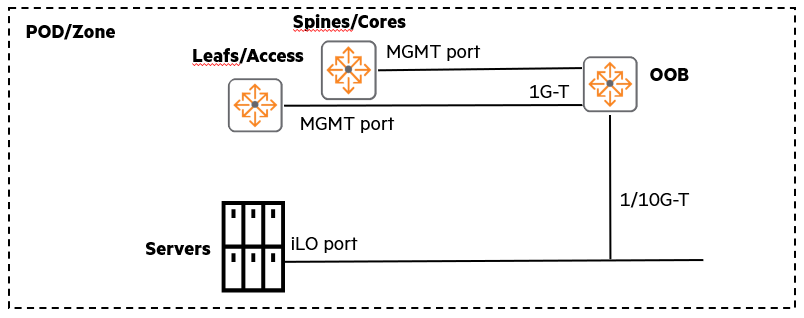
Now let's take a closer look at this OOBM network.
What is the OOBM Network?
OOBM Networkis a critical component commonly deployed in most data centers.
This network is SeparateIt is composed of very Simple network, to equipment such as servers or switches. “Out-of-band” connectionIt provides.
This is the main communication network Even if there is a problem with the in-band network, Allows administrators to access the equipment and troubleshoot issues.
Features of OOBM Switch
Switches in OOBM networks typically do not require the same extreme performance as data network switches.
mostly Provides only simple connectivityBecause you can do it.
Typically, switches with 1Gbps RJ-45 ports are widely used.
However, please note that some high-end servers/systems, such as HPE Synergy, may require 10Gbps connectivity.
Advantages of OOBM Network
- Separate network: A separate OOBM network is built in parallel with the in-band network.
- Provide remote/administrative access: Even when there is a problem with the in-band network Access and manage equipment remotelyIt serves as an emergency exit.
- Relatively low importance: Even if there is a problem with the OOBM network, the application itself continues to operate on the in-band network, so it is relatively less critical than the in-band network.
OOBM network architecture
The picture below is Star topologyShows an example of an OOBM network.
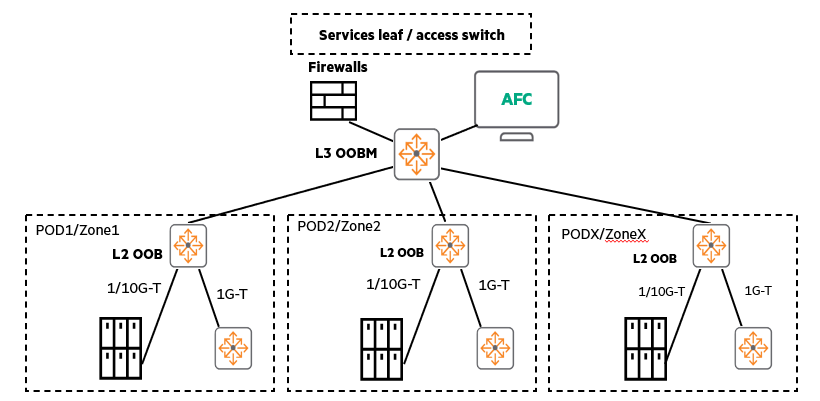
When using multiple PoDs (in-data center modules), these OOBM networks can grow into a star topology, with the L2 zone extending to the L3 core OOB switch. (You can also add VSXs or VSFs for high availability (HA) if desired.)
In this situation, HPE Aruba Networking Multi-Edit SoftwareYou can conveniently manage AOS-CX switches by distributing them.
Best Practices for OOBM Networks
- Star topology recommended: All equipment is connected around a central switch
- Add a firewall: To provide additional network security
- L2 EoR OOBM switch can be deployed within the POD
- Centralized L3 OOBM: L3 OOBM default gateway connects to service leaf or access switch
- Ideal location for Multi-Edit Software: The OOBM network provides an ideal location to deploy Multi-Edit Software, which manages AOS-CX switches.
The OOBM network is a small but critical component that significantly improves the stability and resiliency of data center operations.
Because it provides the only avenue for administrators to intervene when a problem occurs in the main network.
This time, we looked at DCI, which can connect multiple data centers, and OOBM, which is configured separately for management purposes.
The content is not that difficult, but since it is ultimately a continuation of the previous training content, you will need to fully understand the previous training content.
The architecture, structure, and technology of data center networks will continue to evolve, so please familiarize yourself with all the previous training content before moving on to the next section.
- Dense Wavelength-Division Multiplexing ↩︎
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol ↩︎
- Virtual Switching eXtension ↩︎
- Link Aggregation Groups ↩︎
- optical communicationsUnused available for use optical fiberDark fiber originally referred to potential telecommunications infrastructure network capacity. ↩︎


