While today's cybersecurity landscape is rapidly evolving, existing security models remain inadequate to keep pace with increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. One of the biggest trends in corporate security today is the shift from outdated VPNs to Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA).
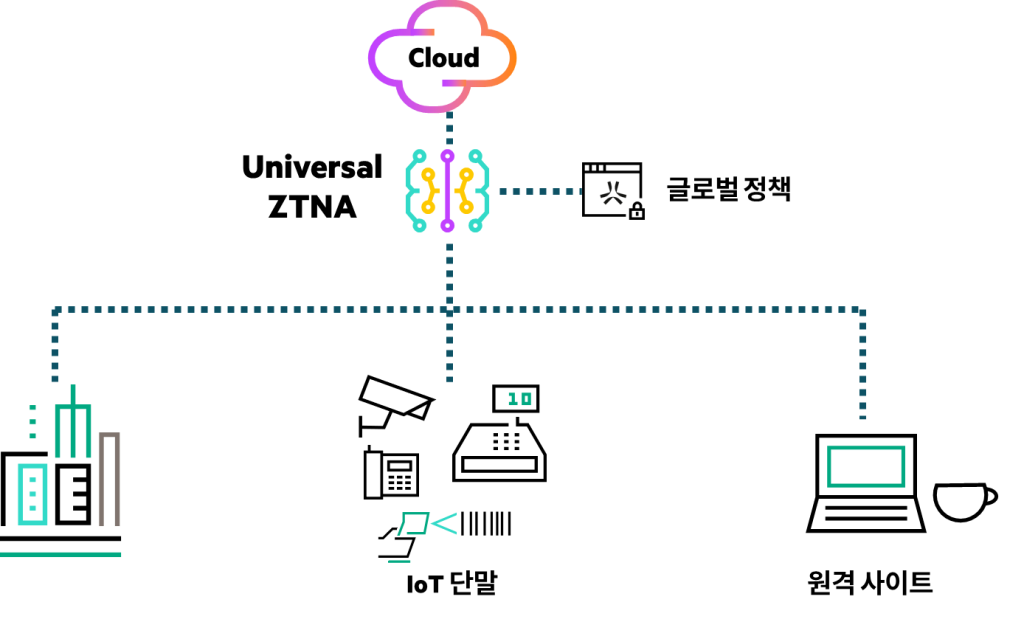
VPNs, which have been a key component of remote access security for years, are no longer considered "security" but rather a "threat" due to the sophistication of cyberattacks and the widespread adoption of hybrid work. In contrast, ZTNA offers a more secure and flexible approach, perfectly suited to the modern security environment.
The Risks of Existing VPNs
VPNs were designed in a time when network boundaries were clear.
When a remote user connects, they are granted broad access to the entire corporate network, and once authenticated, they are completely trusted. However, this outdated trust model has been repeatedly exploited by cybercriminals.
The main risks of traditional VPNs are:.
- Overly broad permissions: Once access is granted via VPN, users can freely move around the entire internal network, which can lead to uncontrollable damage if the network is breached.
- Frequent security breaches: VPN vulnerabilities are the most frequently exploited attack vector by cybercriminals. Attackers focus on outdated VPN equipment and weak authentication systems.
- Low performance and scalability: VPNs introduce latency and have limitations in handling large numbers of remote users simultaneously, resulting in a frustrating user experience.
These risks are causing many companies to re-evaluate their remote approach.
Let's take a look at three key reasons why enterprises are migrating to ZTNA as a more secure alternative.
1. ZTNA eliminates blind trust and reduces attack vectors.
As mentioned earlier, the biggest drawback of VPNs is that they operate on the basis of 'trust'.
If an attacker gains access to your network through stolen accounts, phishing, or VPN vulnerabilities, they can escalate their privileges and move across the network, causing significant damage.
ZTNA, on the other hand, follows a strict principle of 'never trust, always verify'.
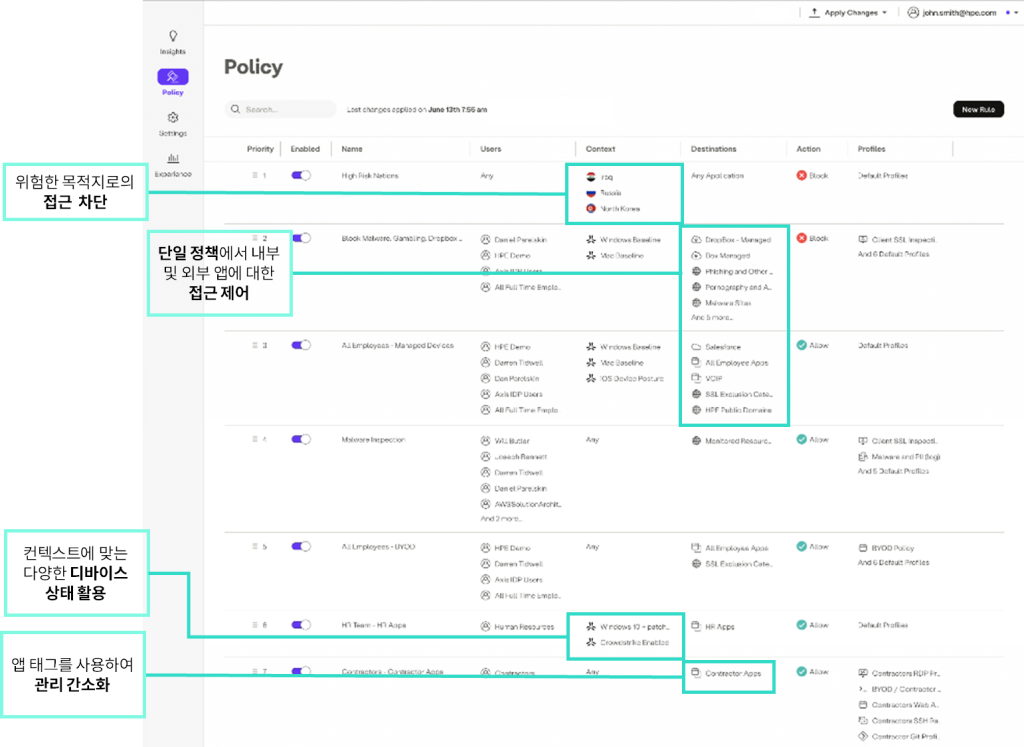
We individually verify every access request to ensure:.
- Users must go through authentication and authorization procedures before accessing specific applications or resources.
- We apply the principle of least privilege to minimize potential damage even if your account is compromised.
- Microsegmentation allows users to access only the specific applications they need, preventing the entire corporate network from being exposed to the outside world.
If you introduce ZTNA Dramatically reduces a company's attack surface This can make it much more difficult for cybercriminals to exploit internal systems.
2. ZTNA prevents VPN vulnerabilities and security breaches.
VPN hacking incidents have become surprisingly frequent recently.
Cybercriminals are targeting VPN infrastructure, the gateway to corporate networks.
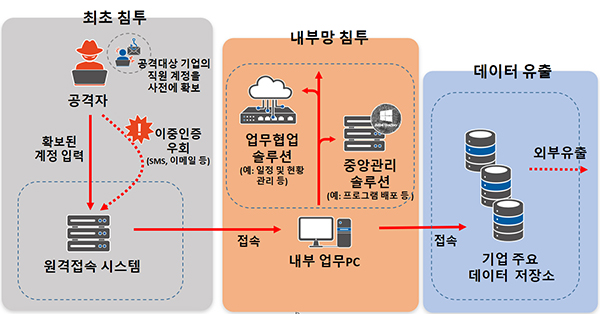
Some serious security issues associated with VPNs include:.
- Account theft and phishing: It's common for attackers to steal or guess VPN login information to gain access to internal resources.
- Exploiting unpatched VPN devices: Many companies fail to patch their VPN equipment in a timely manner, leaving them exposed to known vulnerabilities.
- Ransomware and Data Breach: Some notorious ransomware attacks exploit VPN vulnerabilities to infiltrate and spread malware throughout the network.
ZTNA is a VPN tunnel Identity-based access controlEliminate these risks by replacing them with:.
Instead of simply allowing network access, the ZTNA solution allows for the identification of device status, location, and risk level. Flexibly evaluate users and devices based on contextual informationThis approach makes it much more difficult for attackers to exploit access points.
Additionally, ZTNA solutions Multifactor Authentication (MFA), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), And security information and event management (SIEM) Integrates with tools to provide greater security visibility and control.
3. ZTNA provides better performance and user experience.
Traditional VPNs weren't designed with today's cloud-first, hybrid work environment in mind.
As businesses adopt SaaS and remote work, VPN-based access models are causing significant performance degradation.
Common VPN performance issues include:.
- Network congestion: "Backhauling" all remote traffic back to a centralized VPN gateway introduces latency and slows down access to cloud apps.
- Low scalability: VPNs have limitations in efficiently supporting large numbers of remote users, leading to connection drops and service interruptions.
- Frustrating user experience: Employees frequently disconnect and reconnect, or apps slow down, reducing productivity.
ZTNA centralizes traffic through VPNC1We solve these problems by connecting directly and securely to the application without going through .
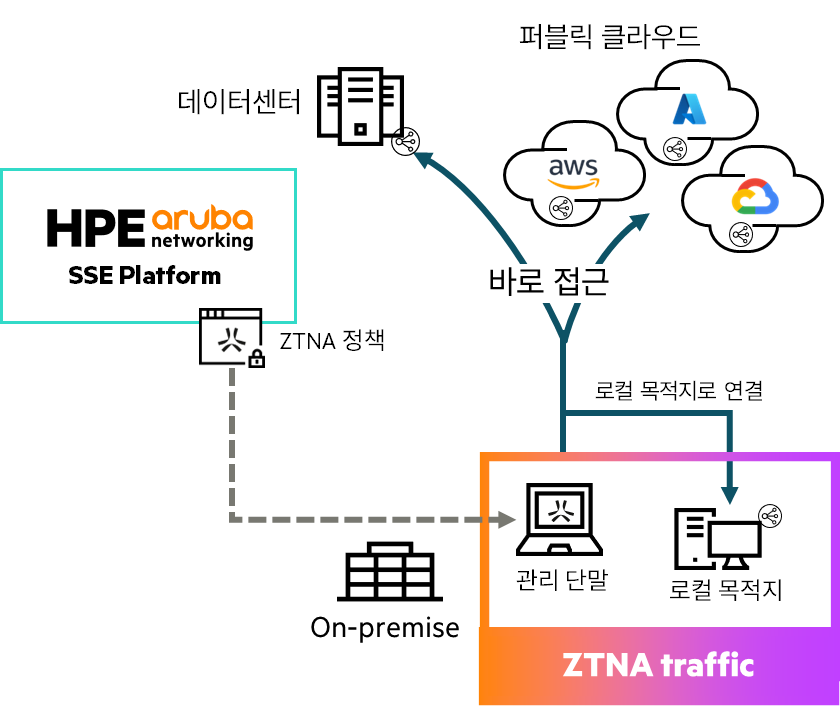
ZTNA, being cloud-based, offers the following advantages:.
- Connect to cloud and on-premises apps without unnecessary bottlenecks. Faster and more direct access
- Seamless scalabilityEasily accommodate remote workers and distributed teams
- For all access requests Consistent security policyApplying it secures both security and convenience
conclusion
The transition from legacy VPNs to ZTNA isn't just a new fad; it's a necessary evolution in cybersecurity.
Once considered essential for secure remote access, VPNs are increasingly becoming recognized as serious security risks due to outdated trust models and frequent vulnerabilities.
ZTNA offers a fundamentally better approach that eliminates blind trust, reduces attack vectors, and strengthens overall security posture. Through granular identity-based access control, ZTNA mitigates common VPN risks while providing a more scalable and user-friendly experience.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, companies that fail to modernize their remote access strategies risk falling behind.
Implementing ZTNA goes beyond simply strengthening security to ensure a smoother and more reliable experience for your employees.
This is precisely why ZTNA is clearly the future of secure remote access.
- VPN Concentrator: It handles VPN connections, establishes secure tunnels, and encrypts and decrypts traffic, acting as a centralized management point for VPN networks. ↩︎


