From AOS-CX version 10.13 A feature called Feature PackThis is new.
Advanced features are available through an additional software license subscription called a Feature Pack.
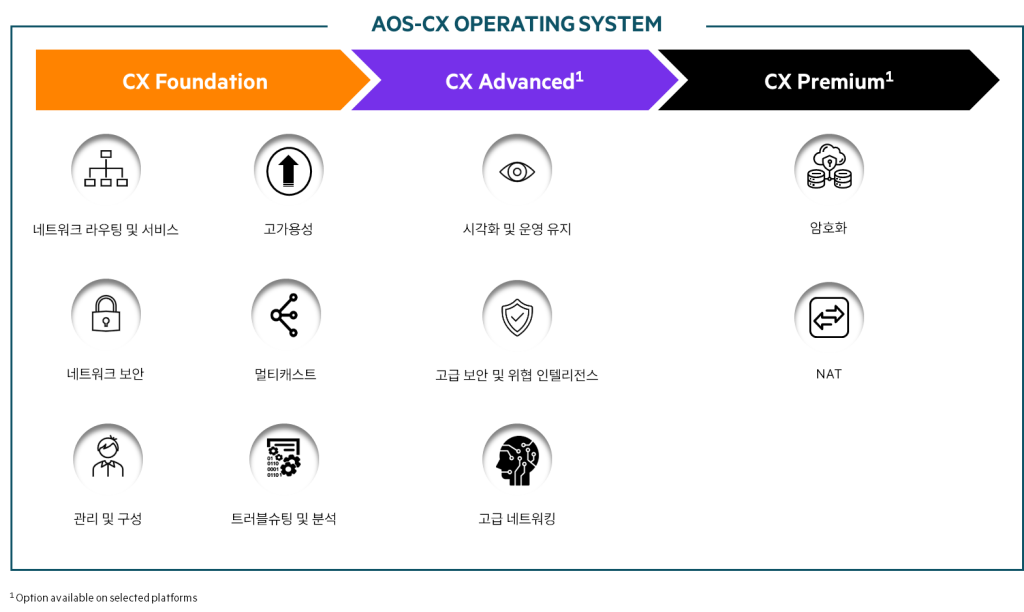
Feature Pack is Advanced와 Premium There are two things.
Premium is the license required to activate the NAT and IPSec functions of the CX 10000 switch.
Other Feature Pack features are available in Advanced.
By subscribing to the Advanced Feature Pack, you can enjoy the following features:.
- WAN MACsec
- Reflexive Policy

- ABP (Application-Based Policy): Application-specific access control policies identified through the App Recognition feature
- Container
Today, I'd like to talk about installing container images inside the CX switch.
What is a Container?
Container technology is one of the server virtualization technologies.
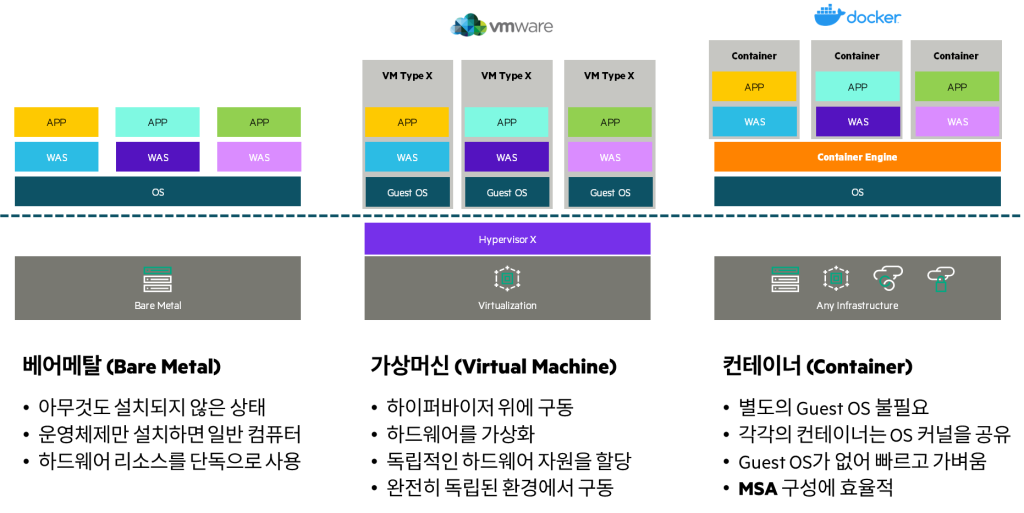
Hypervisor technologies such as VMware place a significant burden on resources and operations because each VM's OS runs independently.
However, containers solve the above problem because they do not require such a guest OS and share the kernel between containers.
These advantages allow containers to be much lighter, faster to deploy, and take up much less memory than traditional virtualization technologies.
This allows you to quickly and easily run multiple instances of virtual environments independently on a single host server.
Why do switches need container technology?
So why would this server virtualization technology be needed on a switch?
Why would you ever need to upload a container image to a switch?
Containers are typically used to deploy lightweight services, such as web application firewalls (WAFs), reverse proxies like NGINX and Traefik, or simple DHCP/DNS servers. These services run on dedicated container hosts, such as physical servers.
That is, since the AOS-CX switch is a Linux-based OS, it can also run on AOS-CX.
Let's look at some use cases.
- Network Monitoring: Collecting metrics from other network devices (Prometheus)
switch(config-container-prometheus)# mount 1 switch(config-container-mount-1)# source usb /data switch(config-container-mount-1)# destination /prometheus switch(config-container-mount-1)# exit switch(config-container-prometheus)# mount 2 switch(config-container-mount-2)# source usb /config switch(config-container-mount-2)# destination /etc/prometheus switch(config-container-mount-2)# exit- API Gateway: Deploy a lightweight API server to automate tasks.
switch(config-container-kong)# mount 1 switch(config-container-mount-1)# source usb /config switch(config-container-mount-1)# destination /etc/kong switch(config-container-mount-1)# exit- DHCP Server: Deploying a DHCP server container at the network edge
switch(config-container-dnsmasq)# mount 1 switch(config-container-mount-1)# source usb /config switch(config-container-mount-1)# destination /etc/dnsmasq switch(config-container-mount-1)# exit switch(config-container-dnsmasq)# mount 2 switch(config-container-mount-2)# source usb /leases switch(config-container-mount-2)# destination /var/lib/dnsmasq switch(config-container-mount-2)# exit- Clone the site: Deploy a lightweight replication service to copy files from one location to another without deploying servers in each location.
- Testing Services: A simple service for checking network connectivity or performance. (iPerf)
Benefits of Installing Container Images
Running these applications on switches as container images can have several advantages.
Containers on AOS-CX switches leverage existing infrastructure and eliminate the need for additional equipment. Provides significant cost savingsdo.
These settings reduce unnecessary maintenance or updates. Very flexible and easy to troubleshootdo.
Moreover, unlike traditional servers, applications on switches are difficult to access and cannot be easily removed. Enhanced securityIt will work.
And by placing applications closer to the edge, we reduce latency and bandwidth usage. Increase response speed.
Consolidating data on the switch minimizes unnecessary connections to servers. Optimize overall network performancedo.
AOS-CX Container Architecture
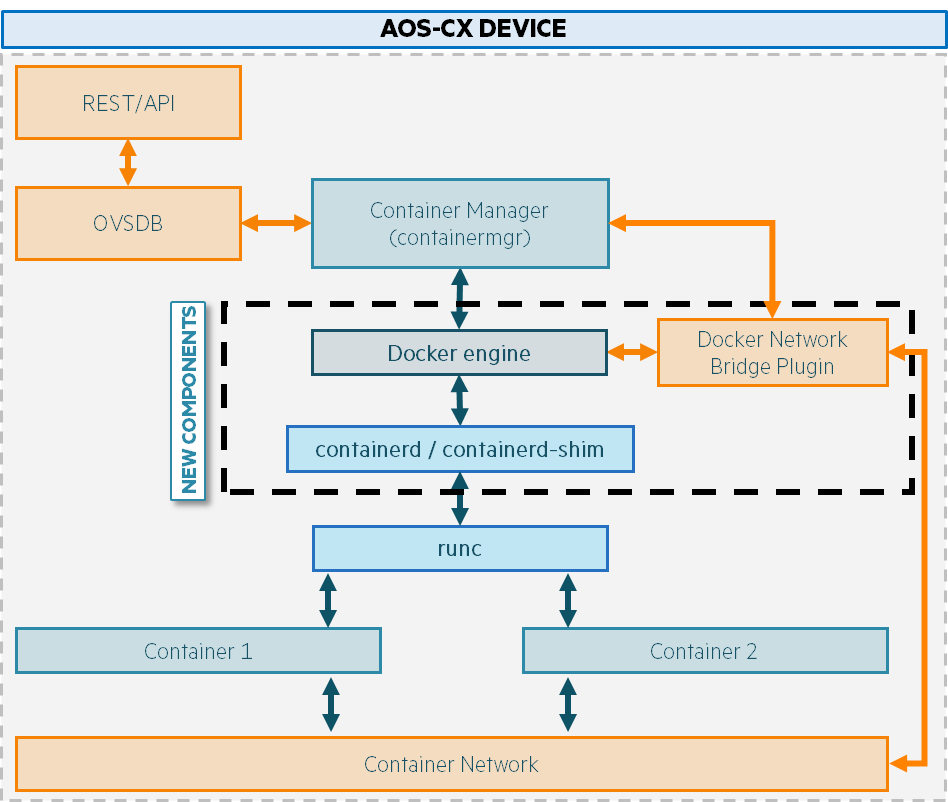
There are several components within the AOS-CX operating system for deploying and running container images.
1. Docker Engine: Key processes that provide an interface between the CX switch and the container infrastructure
2. Container Manager: The main process that manages the container lifecycle, responsible for loading, starting, and passing configuration to running containers.
3. RUNc: A container runtime is a software component responsible for running containers, allocating the underlying operating system kernel and resources to the containers.
4. Conainerd/containerd-shim: Containerd is the container runtime used by Docker to manage the container lifecycle in CX.
5. Container network interface: Provides consistent and reliable networking by ensuring communication between containers and with other network resources.
6. Docker Network Bridge Plugin: Allows bridge network configuration for containers deployed with Container Manager
Docker will take on the role of container manager, meaning you'll be able to leverage a richer, more comprehensive ecosystem.
AOS-CX 10.16.1005 uses Docker 25.0.2-ce version.
3. Like Kubernetes or Openshiftrd Docker orchestration of CX is not possible with Party solutions.
Container network connection
Container images provide connectivity through the network VRF associated with the container image.
You can only configure one VRF per container, and configuring additional VRFs may result in container deployment failures.
CX-Device# show container
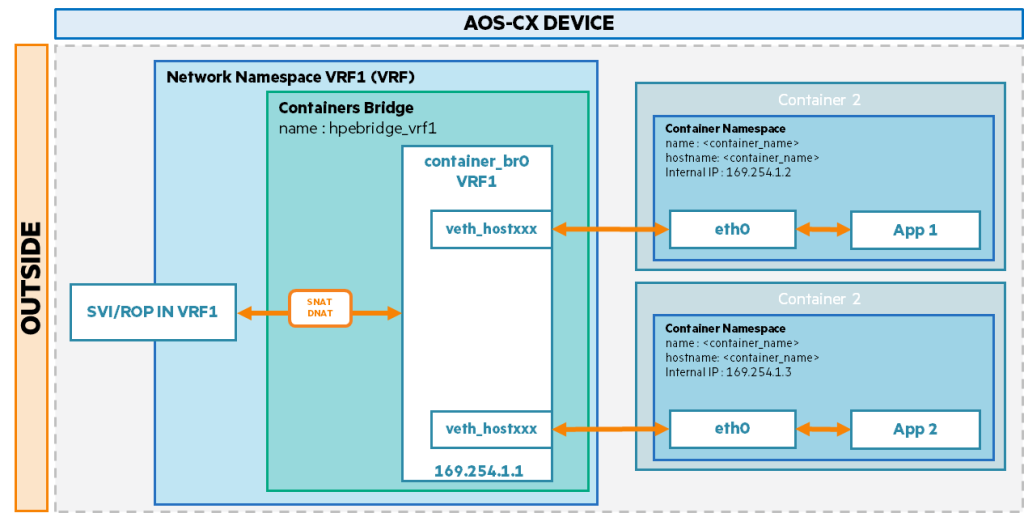
Container: app2 Container status: configuration failed Container status reason: container has more than one network VRFConnecting networks using a single VRF
Each container has its own internal namespace, and its Ethernet interface (eth0) is connected to a container bridge that is part of a specified VRF.
This allows you to bridge traffic between your environment and the outside world (host/network) using source NAT (and destination NAT for bidirectional communication).
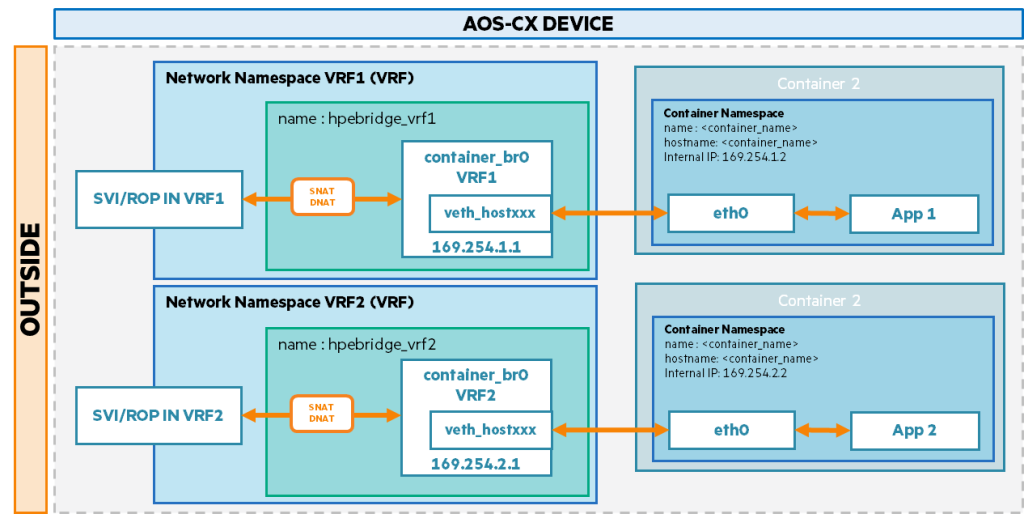
Connecting networks using different VRFs
When containers are connected to different VRFs, each VRF (network namespace) has its own container bridge (container_br0).
Each network namespace uses a different IP subnet.
Deploying container images
Now, let's look at an example of actually deploying a container image.
The container manager uses RUNc as its launch infrastructure.
Therefore, the recommended way to manipulate container images for CX switches is to use Docker.
If you have an x86 system as your development machine, you can build an image for the switch directly using the appropriate Docker image file.
docker build –t . docker save –o .tarIf it is ARM architecture, you can use the above command or select the cross-compile build option.
This requires Docker version 19.03 or later.
docker version export DOCKER_CLI_EXPERIMENTAL=enabled docker buildx create --name arm_builder docker buildx use arm_builderTo build the image and save it as a file, run the following command inside the Docker file directory:.
docker buildx build --platform linux/arm64 -t --load . docker save -o .tarTo install an unsigned container image on a switch: allow-unsigned A command is required.
switch(config)# container demo
The feature being used requires a AOS-CX Advanced Software Feature Pack. For more information, refer to the AOS-CX Feature Pack Deployment Guide. switch(config-container-demo)# image-location http://10.0.14.186:8080/containers/container.img vrf default allow-unsigned
Allowing unsigned container images poses a potential security risk that can impact both the current device and the entire network. By allowing installation of unsigned applications, you are accepting and accepting these risks. HPE shall not be responsible for the consequences of your actions and disclaims all liability. Continue (y/n)? yThe created container image is show container You can check it with the command.
Switch# show container Container : demo Container status : administratively disabled Manifest status: no image Image status : verified Image version : <1.0.0> Image location VRF : default Image location URL : http://10.0.14.186:8080/containers/container.img CPU limit : 10% Memory limit : 256 MB VRFs : defaultStarting with AOS-CX version 10.16.1005, images are no longer downloaded immediately when a container is created.
If you do not activate the container, the CX switch will not automatically download the image.
switch(config)# container demo
switch(config-container-app1)# enable
switch(config-container-app1)# show container demo
Container: demo Container status: operational <----- Snipped ----->Setting environment variables
If your container image requires special settings, you can also set environment variables.
Let's install a location tracking middleware container image called Deephub.
Install the Docker image and limit the memory to 3000MB.
switch(config)# container deephub
switch(config-container-deephub)# image-location http://10.0.0.1:8000/deephub.tar vrf default allow-unsigned
switch(config-container-deephub)# restrict memory 3000Configure VRF settings and port mapping to connect container networks.
switch(config-container-deephub)# network vrf default
switch(config-container-network-vrf-default)# preferred
switch(config-container-network-vrf-default)# port-map host-port 7081 container-port 7081 protocol tcp
switch(config-container-network-vrf-default)# exitNow configure the environment variables for Deephub detailed settings.
switch(config-container-deephub)# env SQLITE_TMPDIR value /data
switch(config-container-deephub)# env DEEPHUB_LICENSE_KEY value 6b05c4cf-1733-4b03-96ee-44a3fdeb80e1
switch(config-container-deephub)# env DEEPHUB_HOST value 0.0.0.0
switch(config-container-deephub)# env DEEPHUB_PORT value 7081
switch(config-container-deephub)# env DEEPHUB_CORS value trueInstall the Deephub UI container image in the same way.
switch(config)# container deephub_ui
switch(config-container-deephub_ui)# image-location http://10.0.0.1:8000/deephub-ui-x86.tar vrf default allow-unsigned
switch(config-container-deephub_ui)# restrict memory 3000
switch(config-container-deephub_ui)# network vrf default
switch(config-container-network-vrf-default)# preferred
switch(config-container-network-vrf-default)# port-map host-port 8082 container-port 8080 protocol tcp
switch(config-container-network-vrf-default)# exit
switch(config-container-deephub_ui)# env DEEPHUB_ROOT_URL value http://localhost:9003show You can check the two container images with the command:.
switch(config)# show container
Container: deephub
container status : operational Manifest status : missing Manifest status reason : The container image does not include a manifest file Image status : allowed without signature Image location VRF : default Image location URL : http://10.0.0.1:8000//deephub.tar CPU limit : 10% Memory limit : 3000 MB VRFs : default Environment variables: SQLITE_TMPDIR value /data DEEPHUB_LICENSE_KEY value 6b05c4cf-1733-4b03-96ee-44a3fdeb80e1 DEEPHUB_HOST value 0.0.0.0 DEEPHUB_PORT value 7081 DEEPHUB_CORS value true Encrypted environment variables: Network: VRF name : default Preferred : yes Port map : 7081:7081/tcpswitch(config)# show container
Container: deephub_ui
Container status : operational Manifest status : missing Manifest status reason : The container image does not include a manifest file Image status : allowed without signature Image location VRF : default Image location URL : http://10.0.0.1:8000//deephub-ui-x86.tar CPU limit : 10% Memory limit : 3000 MB VRFs : default Environment variables: DEEPHUB_ROOT_URL=http://localhost:9003 Encrypted environment variables: Network: VRF name: default Preferred: yes Port map: 8082:8080/tcpThis is a demo video of the installation using the example above.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter error messages while using container images, please refer to the information below.
first of all Container Status Here is a description of the value.
- Down: A prerequisite for container initialization is missing.
- initializing: Container initialization and configuration verification in progress
- operational: The container is running
- network failed: Network provisioning failed
- execution failed: Container execution failed
- configuration failed: User configuration failed
- disabled: Deactivate container
- exited: The container has finished running and is terminated.
Next is the container Image Status Here is a description of the value.
- no image: Container image URL not provided
- downloading: Downloading container image
- downloaded: Container image download successful
- download failed: Container image download failed
- verified: Container image signature verification succeeded
- verification failed: Container image signature verification failed
- allowed without signature: No signature for container image, but allowed
In addition show logging -c container You can check various event logs through commands.
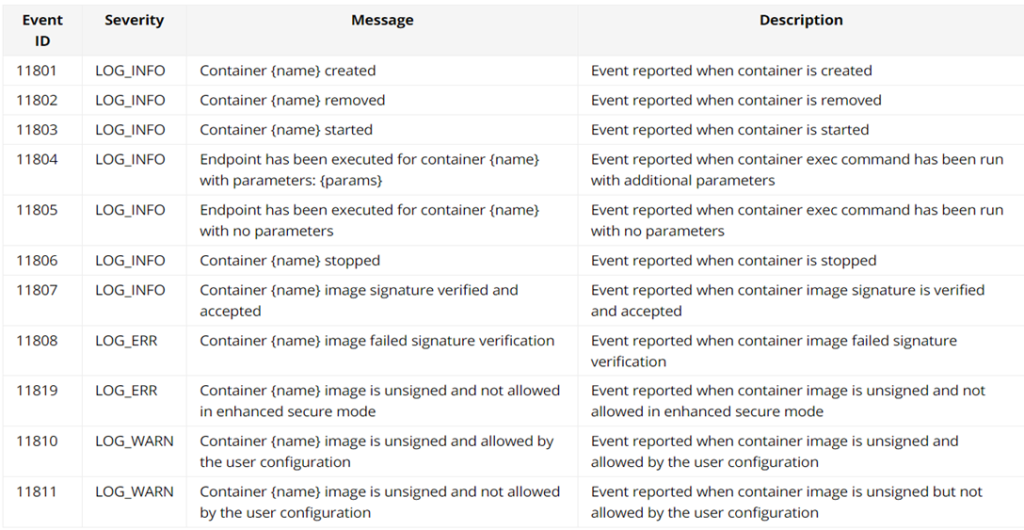
Container Support Platform
Deploying, installing, and operating container images is not supported on all AOS-CX switches.
You can check whether each switch model is supported in the table below.
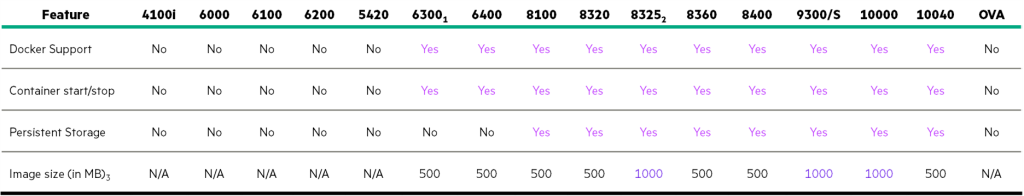
reference: CX 6300L is not supported. CX 8325 includes 8325P and 8325H.
Installing an application on a network switch may be an unfamiliar concept.
However, recent switches are equipped with server-like physical hardware, such as CPUs, RAM, and SSDs.
Installing applications directly inside the switch prevents external intrusions and compromises, and reduces the cost of installing additional hardware.
Operate a richer network infrastructure by leveraging various container images.